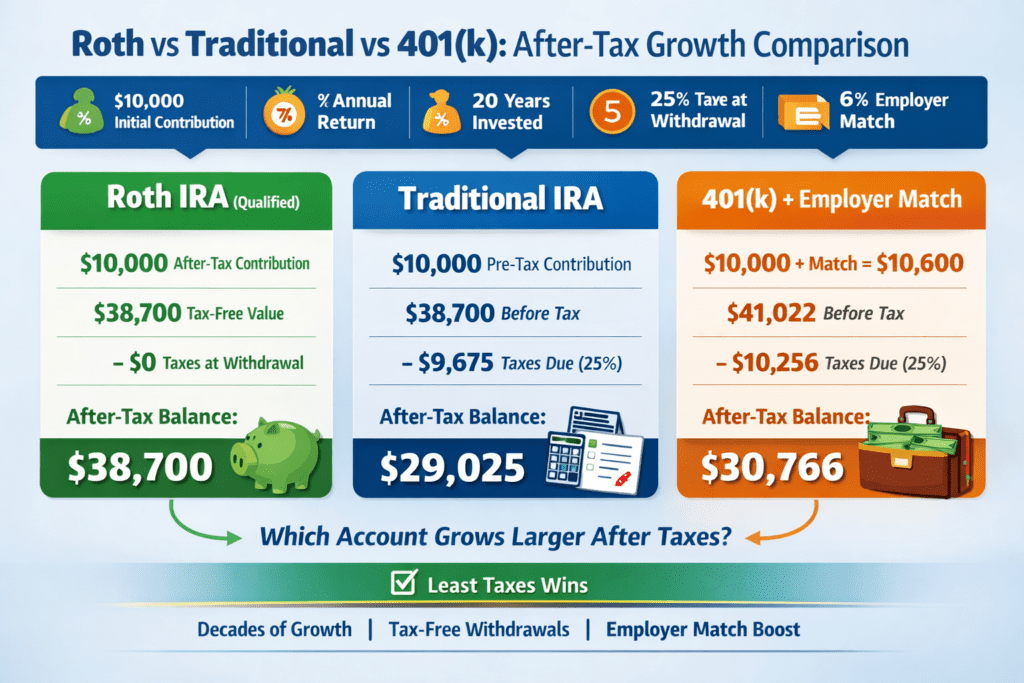
Roth vs Traditional vs 401(k): After-Tax Growth Comparison
Enter the same starting contribution and assumptions for each account type, then see which produces the highest after-tax value at withdrawal. Includes an optional 401(k) employer match.
Keep Exploring Retirement Planning Tools
Visit our calculators hub for additional retirement calculators, including other savings calculators such as 401(k) and Roth tools.
To check current contribution rules and official guidance, please visit the IRS here: IRS: Learn more about HSAs and HRAs .
Don’t forget to read some of our retirement-related articles, including: Gen X Retirement Planning: A 20-Year Guide and Tax Planning for Gen X and Retirees .
Disclaimer: Regulations and laws governing taxes, Social Security, and government-regulated retirement plans can and do change over time. RetireCoast attempts to keep our information current, but we may not always catch something new—particularly at the state and local level. Confirm details before implementing any strategy into your retirement plans.




